What are the causes of scaling in plate heat exchangers?
Plate heat exchanger in chemical production plays an important role in the heat exchanger unit scaling and corrosion leading to insufficient heat transfer, heat exchanger is forced to clean or replace, and seriously affect the safety of production, increasing the cost of business operations. The following author would like to introduce to you the reasons for the scaling of plate heat exchangers.
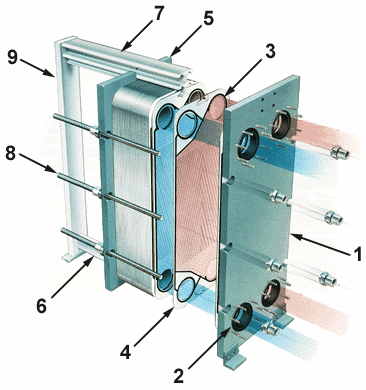
1. Particle dirt
The accumulation of solid particles suspended in the fluid on the heat transfer surface, generally composed of fine particles of silt, dust, insoluble salts, gums, oil, etc.
When water containing these substances flows through the surface of the heat exchanger, it tends to form fouling deposits that form subscale corrosion, providing a breeding ground for certain bacteria to survive and reproduce. When the anti-corrosion measures are not taken properly, they eventually lead to corrosion and perforation of the heat transfer surface and leakage.
2. Biofouling
Biofouling in general refers to microbial fouling with the exception of seawater cooling units. The most common microorganisms in circulating water systems are mainly iron bacteria, fungi and algae.
Iron bacteria can convert water-soluble Fe2+ into water-insoluble Fe2O3 hydrates, which produce large iron oxide precipitation in water and establish oxygen concentration difference corrosion cells that corrode metals.
Also, algae in circulating water systems often form metal surface differential corrosion cells in the water that cause corrosion under the sediment. The block also clogs the lines in the heat exchanger, reducing the flow of water and thus reducing the efficiency of the heat transfer.
3. Crystalline dirt
In the cooling water circulation system, as water evaporates, the concentration of dissolved salts (such as bicarbonates) in the water increases, some salts precipitate due to oversaturation, while some salts precipitate due to thermal decomposition when passing through the heat transfer surface of the heat exchanger. These scales are composed of inorganic salts, crystalline and dense, and are known as crystalline scale.
4. Solidification of dirt
Fouling caused by fluid solidification on the supercooled heat transfer surface. For example, when water is below freezing point and solidifies into ice on the heat transfer surface. Whether the temperature distribution is uniform or not has a big impact on this fouling.
These are the common causes of plate heat exchanger scaling introduced by the author for you, I hope to help you, if you have other aspects want to understand, you can come to consult us.
Related information
- Our quotation for plate heat exchanger, is it really expensive?
- How to buy a quality plate heat exchanger?
- Boiler supporting plate heat exchanger, how much do you know
- Application of Alfa Laval sanitary plate heat exchanger in food processing industry
- Common materials and applicable conditions for plates of plate heat exchangers
- About the correct installation method of plate heat exchanger rubber gasket
Relevant article
- 1
- Can plate heat exchanger be directly used for feed water heating or cooling?
- Why the heat transfer efficiency of plate heat exchangers in the heating industry is low
- How to determine the size and angle of plate heat exchanger plate?
- What is the proportion of pressure drop in the selection of plate heat exchanger?
- Why do we recommend food grade plate heat exchanger for beer brewing and fermentation? What should we pay attention to?
- What is the difference between the hanging holes on the plate of plate heat exchanger?
- What are the applications of plate and shell heat exchanger in the field of petroleum refining
- What is the key to the manufacture of plate heat exchangers with small temperature differences?
- How to descale the plate heat exchanger? What problems should be paid attention to during use?
Latest information
- Heat station supporting plate heat exchanger installation is a technical work, these points should be noted
- Sulfuric acid and other corrosive media for industrial plate heat exchanger requirements are what
- Simple and effective chemical cleaning method of coal chemical plate heat exchanger, can effectively improve efficiency
- A high-quality petrochemical plate heat exchanger in the production of what to consider
- These causes of chemical plate heat exchanger gasket aging you may not know
- Chemical plant plate heat exchanger, sulfuric acid cooling needs attention
- High-end plate heat exchanger customization, specifically for your special working conditions
- The working principle of gasket type industrial plate heat exchanger and the scenarios of its use are worth knowing in depth
- Still worrying about the wholesale price of industrial plate heat exchangers? An article to make you no longer tangled
- The original lubricant in the chemical plate heat exchanger plays so many roles!